Energy-Efficient Homogenization: Reducing Costs in Large-Scale Production
In modern manufacturing, energy efficiency has become a top priority. Rising energy prices, stricter environmental regulations, and growing awareness of sustainability all push industries to adopt more efficient technologies. For companies involved in large-scale production of food, beverages, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and chemicals, homogenization is a critical process that directly impacts product quality and stability. However, traditional homogenization methods often consume significant amounts of energy. This has led to a growing demand for energy-efficient homogenizers, which not only reduce operating costs but also contribute to environmental responsibility.
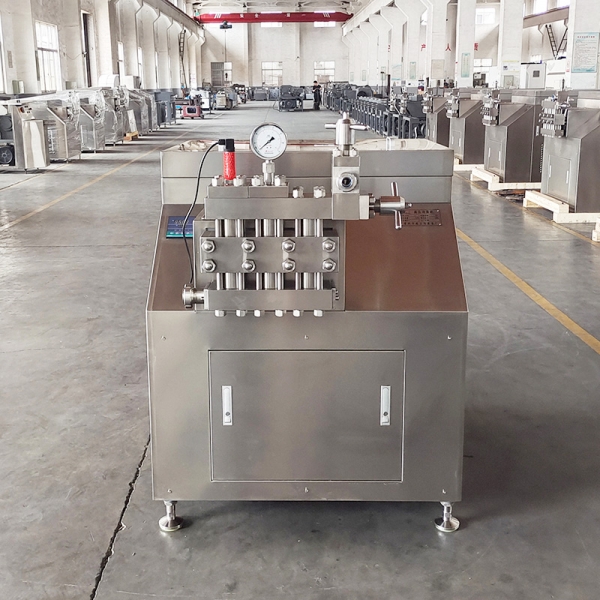
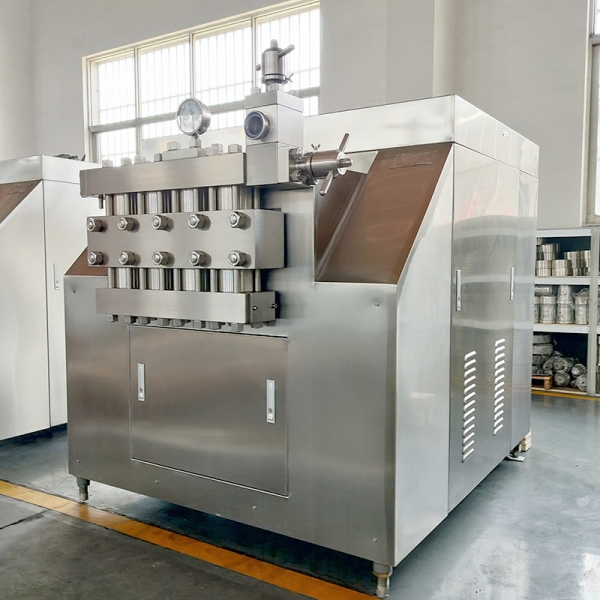
Homogenization is the process of breaking down and evenly dispersing particles in a liquid, creating a stable and uniform mixture. In industries such as beverages, homogenization ensures smooth textures and prevents separation. In pharmaceuticals, it improves drug solubility and bioavailability. In cosmetics, it ensures consistent emulsions in creams and lotions. While homogenization is vital for product performance, it is also energy-intensive, particularly in large-scale production where high pressure and continuous operation are required. This makes efficiency a key factor in equipment selection.
Conventional homogenizers typically rely on high pressures, powerful motors, and continuous operation, all of which consume large amounts of electricity. In large factories running multiple production lines, the cumulative energy consumption can be enormous. Moreover, inefficient designs may waste energy through heat loss, friction, and poorly optimized flow patterns. This not only raises operational costs but also contributes to carbon emissions. As industries aim to balance productivity with sustainability, these energy challenges have become increasingly difficult to ignore.
Energy-efficient homogenization focuses on reducing power consumption without compromising product quality. The main principles include:
Optimized Pressure Control – Using only the necessary pressure for a given product instead of applying maximum levels across all operations.
Advanced Valve and Pump Design – Minimizing energy loss by improving flow dynamics and reducing friction.
Heat Management Systems – Capturing and reusing heat generated during homogenization to lower energy waste.
Automation and Smart Controls – Integrating intelligent systems that adjust parameters in real time based on product characteristics, ensuring efficient use of energy.
By applying these principles, manufacturers can achieve the same high-quality results while significantly cutting energy costs.
Energy costs make up a large portion of production expenses in industries that rely heavily on homogenization. By adopting energy-efficient systems, companies can see substantial cost savings over time. For example, reducing energy consumption by just 10–20% can lead to thousands of dollars in annual savings in large-scale operations. Moreover, efficient homogenizers reduce wear and tear on components, lowering maintenance and replacement costs. Combined, these savings directly impact profitability, making energy efficiency not just an environmental goal but a financial strategy.
In addition to cost savings, energy-efficient homogenization contributes to broader sustainability goals. Lower energy consumption means reduced greenhouse gas emissions, aligning with international environmental standards and corporate responsibility initiatives. Many global companies now publish sustainability reports that track energy usage and carbon footprints. By investing in efficient homogenizers, businesses can improve their sustainability profiles, strengthen brand reputation, and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers and partners.
Energy-efficient homogenization benefits a wide range of industries:
Food & Beverages – Reduced power consumption in large-scale juice, sauce, and plant-based drink production.
Pharmaceuticals – Efficient production of nanoemulsions, suspensions, and injectable formulations.
Cosmetics – Lower costs in producing stable creams, lotions, and serums.
Chemicals & Industrial Fluids – Improved efficiency in dispersing pigments, lubricants, and adhesives.
For each of these sectors, efficiency ensures high-quality products while keeping costs under control.
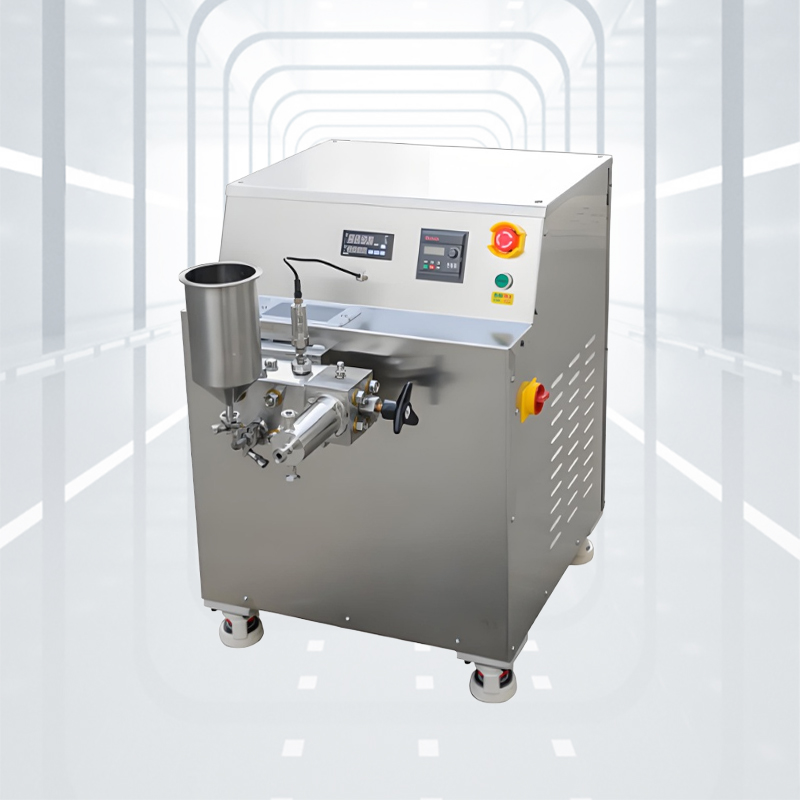
One effective way to achieve energy efficiency is through OEM and ODM customization. Instead of relying on standard models, businesses can work with experienced manufacturers to design homogenizers tailored to their processes. Custom solutions can optimize motor size, pressure levels, and flow patterns to minimize energy usage. For example, Changzhou Chaoli Homogenizer Factory provides customized equipment designed to meet industry-specific requirements while reducing energy waste. Such partnerships enable businesses to balance performance, efficiency, and long-term reliability.
The future of homogenization lies in even greater efficiency and digital integration. Developments include:
IoT-enabled Smart Homogenizers that monitor energy usage in real time.
Predictive Maintenance Systems that reduce downtime and energy waste.
Eco-friendly Designs with improved heat recovery and reduced noise.
Hybrid Systems that combine traditional and innovative homogenization methods to achieve maximum efficiency.
As industries continue to scale up, adopting these future technologies will be crucial for staying competitive.
Energy-efficient homogenization is no longer an option but a necessity for large-scale production. By reducing power consumption, manufacturers can significantly cut costs, improve profitability, and strengthen sustainability efforts. Through advanced designs, automation, and customized solutions, homogenizers are evolving into smarter, greener, and more cost-effective machines. For businesses seeking long-term success, investing in energy-efficient homogenization is a practical step toward balancing economic growth with environmental responsibility.






